Most health nerds are familiar with the idea of boosting their immune system to maintain optimal health by taking supplements when defences are low. But, what if there was another physiological system in the human body that, when deficient, could disrupt your overall health, i.e. your body’s homeostasis? That is where the endocannabinoid system (ECS) comes into play. While many still condemn the use of cannabis as medicine, don’t let people tell you there’s a lack of scientific backing for cannabis’ medicinal properties.
In a previous article, we briefly discussed research is showing how CBD works in the body, in conjunction with the ECS when it comes to optimal health — which has not only legitimized cannabis as medicine in the public eye, but has also expanded our understanding of human biology and recognition for the special relationship shared between cannabis and the ECS. In this article, we revisit what the ECS is and take a look at why it’s so important to our understanding of all cannabinoids and not just CBD.
The discovery of the Endocannabinoid System
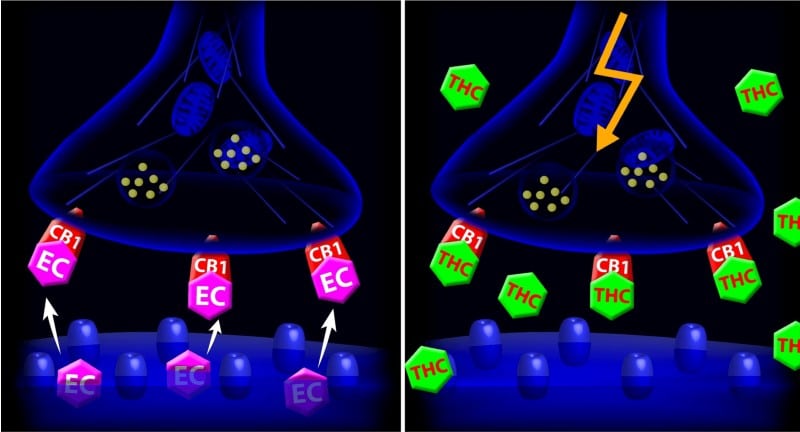
The ECS is a vital molecular system in our body that is responsible for maintaining balance in the body by regulating a multitude of bodily functions. The ECS is comprised of cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2) which, in turn, regulate the synthesis and breakdown of active cannabinoid compounds present in the immune system and nervous system.
Discovered in the early 90’s by scientist and professor Raphael Mechoulam, in collaboration with NIMH researchers William Devane and Dr. Lumir Hanus. Initially, they were trying to find where and how the psychoactive compound in cannabis, THC, binds and interacts with our body. In their findings, they noticed the body produces its own natural compounds that elicited a similar effect to cannabis.