Even though Δ8-THC is only found in small amounts in dried cannabis flowers, it is still seen as one of the major cannabinoids. THC can be converted into Δ8-THC by shifting the position of some of its electrons or even from CBD, through a process called “cyclization”.
The difference between THC and Δ8-THC
Despite THC and Δ8-THC being almost the same, Δ8-THC is less psychoactive than THC. On the other hand, Δ8-THC decays a lot less quickly and is much more stable than THC. That is why Δ8-THC is better suited to study the effects and inner working of THC on humans.
Medicinal benefits of Δ8-THC
Δ8-THC is also a better alternative to THC as a medicine, because it has the same beneficial effects, but is less psychoactive. The medicinal properties of Δ8-THC are:
- Its effectiveness against vomiting and nausea.
- Its ability to relieve anxiety.
- Its ability to relieve pain.
- Its ability to stimulate appetite.
- Its neuroprotective properties.
- Its ability to reduce inflammation.
A scientific summary of Δ8-tetrahydrocannabinol
Δ8-tetrahydrocannabinol (Delta-8-THC) is one of the four major cannabinoids found in cannabis. Despite its natural occurrence in most dried flowers is low (less than 1% of cannabinoid content), a higher amount of this cannabinoid can be obtained through techniques such as extraction, isolation, conversion and refinement.
Delta-8-THC is almost the same as Delta-9-THC
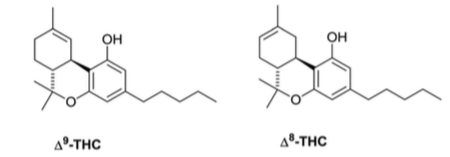
As its name suggests, Delta-8-THC is an analogue of Delta-9-THC (the primary form of THC found in cannabis). It can be biosynthesized from Δ9-THC by a reaction called “isomerization”, which involves a position shift of two sets of electrons (from carbon-9 to carbon-8 of its core-ring – Figure 1), or from CBD by cyclization.
Delta-8-THC is more stable than Delta-9-THC
Despite the similar chemistry and metabolism profiles, Δ8-THC is less psychoactive than Δ9-THC. It is, however, easier and less expensive to prepare and has a much longer shelf-life than Δ9-THC. This compound is chemically more stable than its Δ9-cousin and this would justify the practice of isomerizing Δ9-THC into the more stable Δ8-form. Because of its stability and its ease to synthesis, Δ8-THC has shown to be a better candidate for phytocannabinoid-inspired probes to explore the dynamics and the environment around cannabinoid receptors.
Medicinal benefits of Delta-8-THC
From a medical point-of-view, Δ8-THC shows to have antiemetic (1), anxiolytic (2), appetite-stimulating, analgesic (3), and neuroprotective properties. It has also been shown to be pharmacologically active as an anti-glaucoma agent, despite its topical use is limited, just like Δ9-THC, by its low affinity and solubility in water-based solvents and resinous nature.
Δ8-THC is also effective against corneal pain and inflammation as a result from ocular surface damage. Such anti-nociceptive (4) and anti-inflammatory actions are mediated primarily by the activation of the cannabinoid G-protein coupled receptor (CB1-R), located in the central nervous system. Furthermore, compared to its Δ9 analogue, Δ8-THC has shown to have almost no psychoactive side-effects when administered prior to chemotherapy in cancer patients.