Terpenes and cannabinoids tend to steal the spotlight when it comes to cannabis, but there’s another type of compound that deserves some center stage time – the phytonutrient, flavonoid. Much like the others, these cannabis compounds called ‘cannaflavins’ are responsible for how the plant is perceived, including its physical appearance, but it goes far beyond that.
Flavonoids are members of the most abundant nutrient families and have an excellent reputation for providing benefits to not only the development, but also the consumption of plants such as herbs, fruits, and veggies. Around 6,000 varieties exist in nature, and, despite not being broadly researched, research has proven flavonoids to contain anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-fungal, anti-bacterial, anti-allergic and neuroprotective activity. That said, they may be worth learning about. Below, find out how they work and why you should know about them.
What are flavonoids and what is their purpose?
The word ‘flavonoid’ is derived from the Latin word “flavus” meaning ‘yellow’ or ‘blond’, their color in nature. Without fishing too deep into scientific jargon, the natural-occurring metabolites called flavonoids are found abundant in a variety of plants, including veggies, fruits, and yes our dear plant friend cannabis. They’re members of the largest nutrient families distributed throughout all parts of a plant, including the roots, flowers, stems, leaves, and seeds. By bonding with one another and other compounds, flavonoids can have a highly bioactive impact on the cultivation and nutritional value of a plant.
PROVIDES PROTECTION:
Flavonoids execute essential functions in plants. One purpose of flavonoids is to help protect the cannabis plant, and at a cellular level, serve as regulators of cell cycle progression.
These functions include defense against environmental stressors such as diseases, severe temperature fluxuations, and bacteria, cell growth regulation, as well as attracting pollinating insects. In addition to serving as fungicides, antioxidants and even against harmful insects, as the cannabis plant grows, these compounds protect it from harmful UV rays, operating in areas of plant-growth like UV light filtering system.
GIVES CHARACTER:
In addition to controlling growth processes and protection, flavonoids also provide the unique, vibrant colors and overall outward appearance of each cannabis strain. Beyond providing colorful pigments – and defending against outside factors, research has shown that flavonoids exhibit high biological activity that can have particular health benefits in humans when consuming the cannabis plant.
How do they benefit humans?
Often mentioned in the context of a healthy diet, cannabis consumers can also benefit from consuming these phytonutrients. Many properties in cannabis are synergistic, which means they work together. This is similar when you consider flavonoids and other cannabis compounds apart of the cannabis makeup; the entire plant was created to work as a whole in order to produce the best effects.
When we consume cannabis, flavonoids work similarly to the synergistic activity between cannabinoids and terpenes. By also plugging into CB1 and CB2 receptors, flavonoids, along with other compounds, display a synergy, commonly referred to as the “entourage effect”. Simply put, you get a more beneficial effect when you ingest multiple cannabis compounds together – than just ingesting one at a time. Much like cannabinoids, flavonoids contain unique elements that can influence their metabolic state in the human body (i.e., their absorption, digestion, and biotransformation). And, depending on the compounds they encounter, their ability to exert pharmacological activity relevant to our health is determined by their bioavailability (i.e. how much of the compounds are available for the body to work with). Research conducted on flavonoids points out that most of them all share the same beneficial properties, but also have some unique abilities. The more well-known flavonoids include:
Cannflavin A – Cannabis-specific flavonoid with anti-inflammatory properties, said to be more powerful than those in pain relieving drugs, such as Aspirin and Tylenol.
Cannflavin B & C – Both cannabis-specific flavonoids, and seem to have the same beneficial properties of that of Cannaflavin A, but more research is needed.
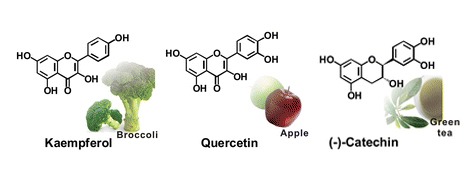
Catechins – Also found in cacao beans, herbal teas and some fruits, this flavonoid contains antioxidants and also offers cardiovascular health benefits.
Kaempferol – Found in a variety of plants, fruits and vegetables (including cannabis), Kaempferol has antioxidizing properties to help reduce oxidative stress in the body. Furthermore, Kaempferol is currently under consideration as a possible cancer treatment.
Orientin – Found in cannabis as well as teas (specifically Rooibos tea), Bamboo- and Palm trees and said to be a powerful antioxidant and free-radical scavenger.
Quercetin – Found in the cannabis plant as well as teas, fruits and vegetables, the Quercetin flavonoid contains tons of antifungal and antioxidant properties.
In conclusion: The future of cannabis science looks colorful and healthy
We may have limited research on the mechanics of flavonoids in cannabis, but the powerful properties of these compounds are seemingly beneficial to us humans — just like the flavonoids in other plants. We’re hopeful that science will develop beyond the human sensory experience and soon discover how the contribution of flavonoids affects all forms of cannabis.